An introduction to improved forest management VM0010 projects
August 20, 2025 - Research
Dynamic baseline methodologies – like VM0045 – are getting a lot of attention in improved forest management carbon projects, and for good reason. These new approaches aim to improve credit integrity by using national forest inventories to create more objective baselines for carbon accounting.
But while attention is shifting to these new methods, Verra’s VM0010 Methodology is still delivering millions of credits, with many more projects in the pipeline. Calyx Global has recently added ratings for credits generated by some of the largest VM0010 projects currently trading in the voluntary carbon market.
What is the VM0010 methodology
Projects developed under VM0010: Methodology for Improved Forest Management: Conversion from Logged to Protected Forest can receive carbon credits for two main activities: preventing planned timber harvest in forests (avoided emissions) and enabling new forest growth (carbon removals). The VM0010 methodology applies broadly to tropical, temperate and boreal forests – unlike ACR’s Improved Forest Management (IFM) on Non-Federal U.S. Forestlands (Version 2.1) or CAR Mexico Forest Protocol v 3.0, which have a limited geographic scope.
Since its initial release in 2011, VM0010 has undergone several updates. Version 1.3 (2016), which is widely used for projects developed and listed prior to 2025, allows baseline scenarios involving clear-cutting or selective logging in both planted and natural forests. The latest update, Version 1.4 (2024), limits baseline scenarios to selective logging in natural forests only. Project activities involving commercial timber harvesting or forest degradation are also explicitly excluded under VM0010.
VM0010 projects in the voluntary carbon market
Nineteen projects developed under VM0010 are currently issuing credits. As of June 2025, VM0010 projects had issued over 13.5 million credits, roughly 5% of all IFM credits across registries. Of these, just over half have been retired, with around 5.1 million tonnes remaining and 1.8M of those issued in 2020 or after.
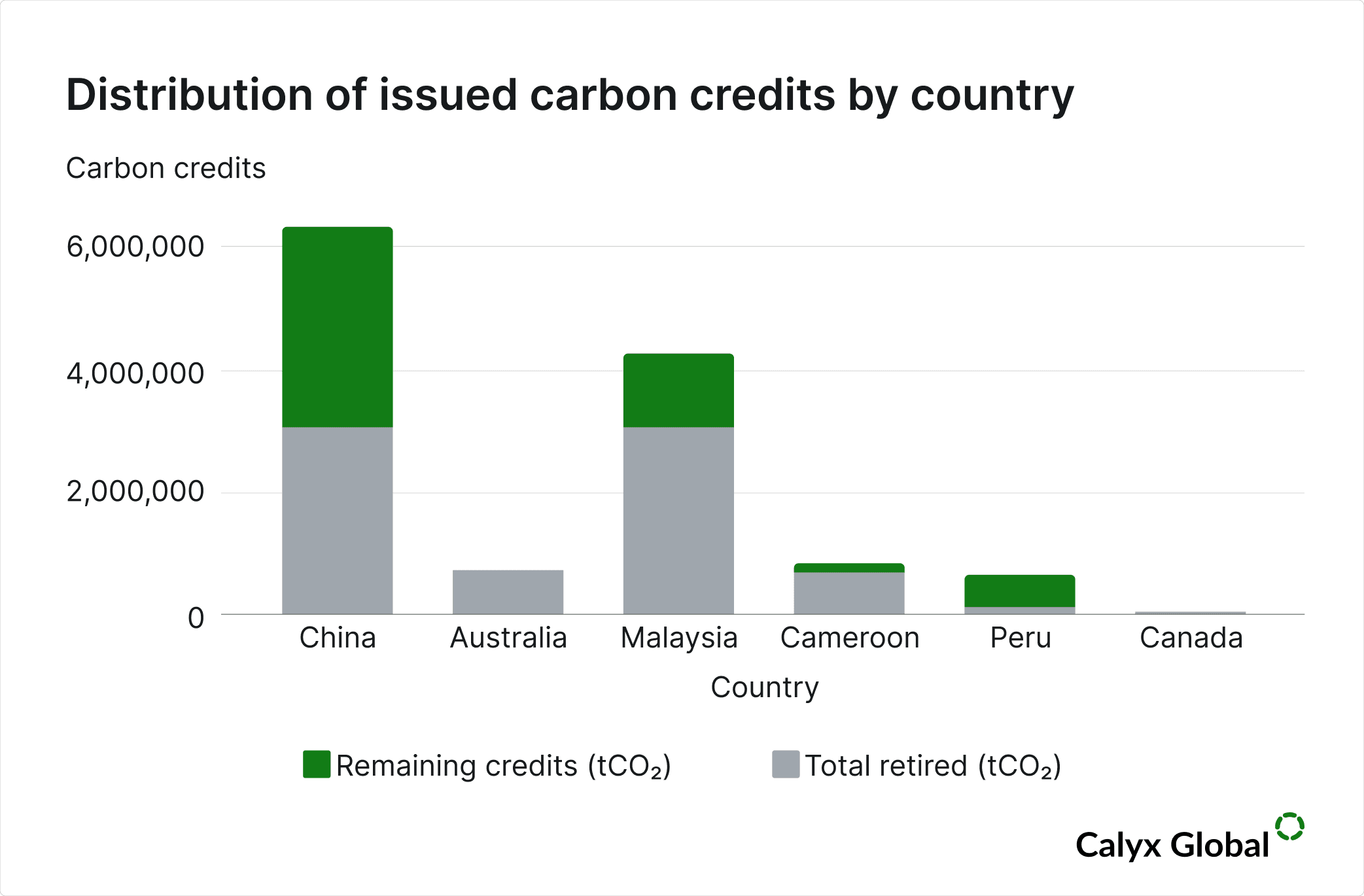
Original data source: Berkeley’s Voluntary Registry Offsets Database (v2025-06)
Among the 19 projects that are issuing credits, 11 are located in China, with four in Australia, and the rest are distributed across Malaysia, Cameroon, Peru and Canada. While China dominates in project count and total volume, Malaysia’s Kuamut Rainforest project stands out as the single largest issuer, with over 4.26 million credits issued. We have rated 32% of all VM0010 credits issued to date.
While attention may be shifting to VM0045 Methodology for Improved Forest Management Using Dynamic Matched Baselines from National Forest Inventories, over 30 projects are still being developed and validated under the VM0010 methodology, particularly in China, Southeast Asia, and parts of Africa and Latin America. If all of these projects come to market, they could generate over 7 million credits annually.
We will keep you informed of both VM0045 and VM0010, as the market for these credits expands. Meanwhile, check out our first VM0010 ratings on the Calyx Global platform.
Citations:
[1]Barbara K Haya, Tyler Bernard, Aline Abayo, Xinyun Rong, Ivy S So, Micah Elias. (2025). Voluntary Registry Offsets Database v2025-06, Berkeley Carbon Trading Project, University of California, Berkeley. Retrieved from: https://gspp.berkeley.edu/berkeley-carbon-trading-project/offsets-database
Keep up with carbon market trends
Get the monthly newsletter and stay in the loop.
Trusted By





